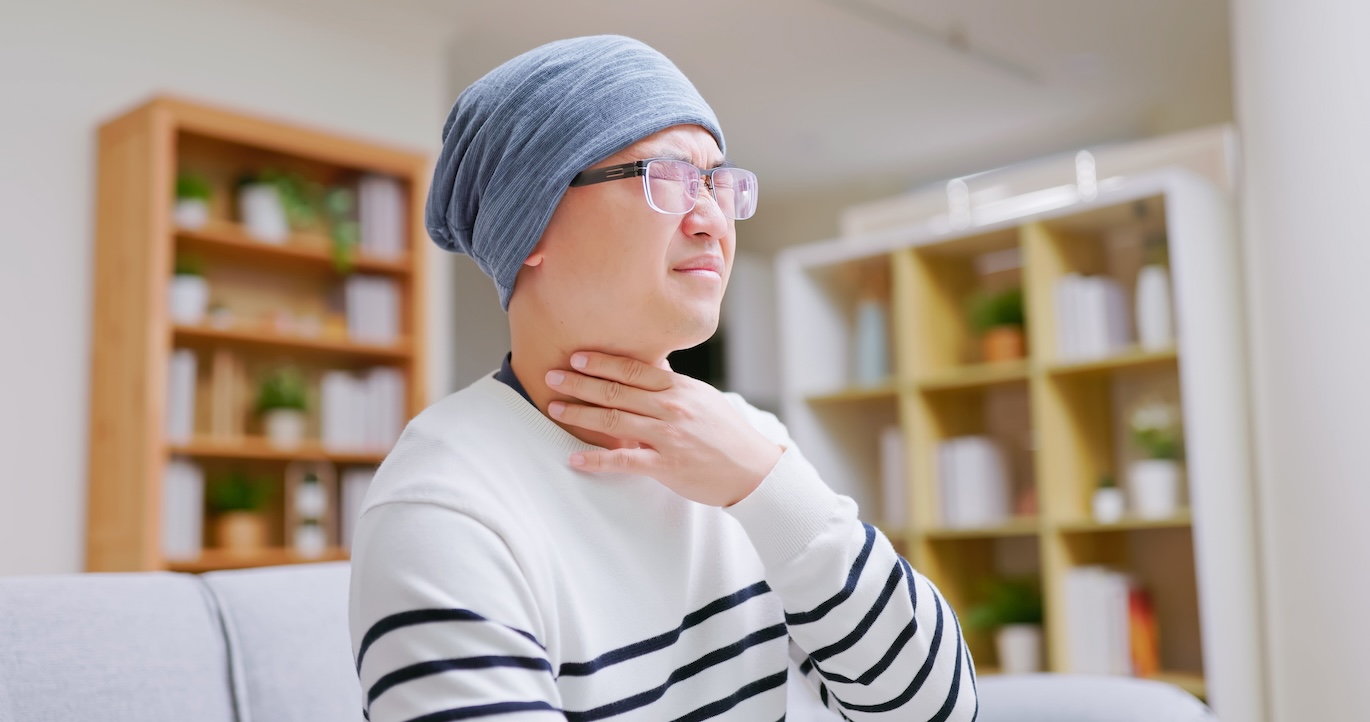
Our team of hundreds of leading cancer physicians and oncology-trained support staff is a trusted partner in returning patients with cancer to good health.
Esophageal Cancer
New Patient Appointment or 214-645-4673
MedBlog
Results: 7 Locations
Digestive Disease
at UT Southwestern Frisco 12500 Dallas Parkway, 2nd FloorFrisco, Texas 75033 469-604-9020 Directions to Digestive Disease at UT Southwestern Frisco, Frisco Parking Info for Digestive Disease
Pancreatic Cancer Clinic
at Cancer Care Outpatient Building 6202 Harry Hines Blvd., 9th FloorDallas, Texas 75235 (214) 645-4673 Directions to Pancreatic Cancer Clinic at Cancer Care Outpatient Building, Dallas Parking Info for Pancreatic Cancer Clinic
Simmons Cancer Center
at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Richardson/Plano 3030 Waterview Parkway, 2nd FloorRichardson, Texas 75080 972-669-7077 Directions to Simmons Cancer Center at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Richardson/Plano, Richardson
UT Southwestern Medical Center at RedBird
3450 W. Camp Wisdom RoadDallas, Texas 75237 214-645-8300 Directions to UT Southwestern Medical Center at RedBird, Dallas Parking Info for UT Southwestern Medical Center at RedBird
Thoracic Surgery
at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Coppell 2999 Olympus Blvd., 3rd FloorCoppell, Texas 75019 214-645-7700 Directions to Thoracic Surgery at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Coppell, Coppell Parking Info for Thoracic Surgery
UT Southwestern Thoracic Surgery at Texas Health Dallas
at Professional 3 8230 Walnut Hill Lane, 204Dallas, Texas 75231 214-645-7700 Directions to UT Southwestern Thoracic Surgery at Texas Health Dallas at Professional 3, Dallas Parking Info for UT Southwestern Thoracic Surgery at Texas Health Dallas