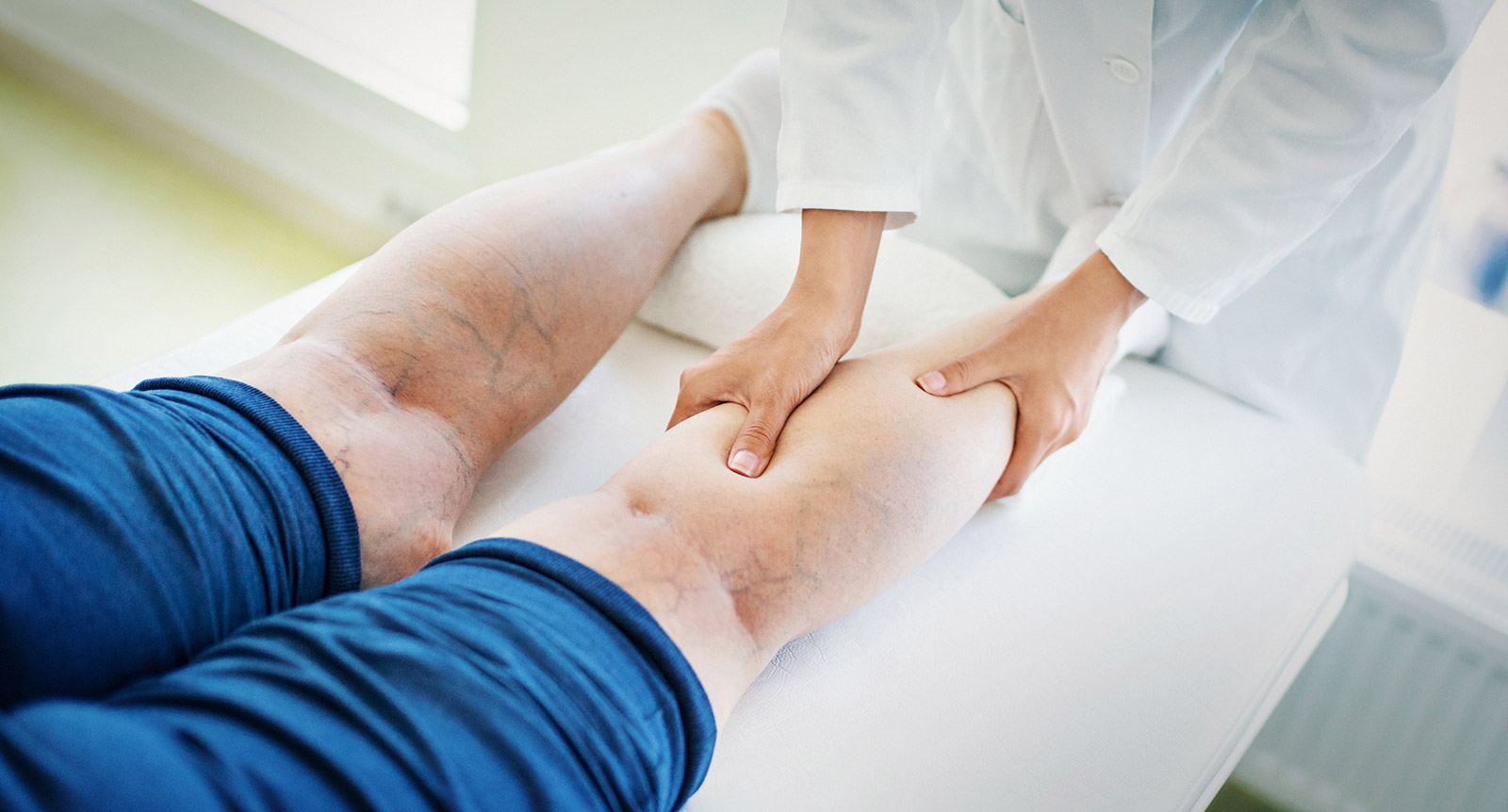
Combining attentive, compassionate care with our extensive clinical and research resources, UT Southwestern's cardiology experts and vascular specialists deliver individualized care within pre-eminent health care facilities.
Venous Disease
New Patient Appointment or 214-645-8300
Results: 4 Locations
West Campus Building 3
2001 Inwood RoadDallas, Texas 75390 214-645-8300 Directions to West Campus Building 3, Dallas Parking Info for West Campus Building 3
Vascular Medicine
at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Park Cities 8611 Hillcrest Road, 2nd Floor, Suite 250Dallas, Texas 75225 214-692-3135 Directions to Vascular Medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Park Cities, Dallas Parking Info for Vascular Medicine
Vascular Medicine
at UT Southwestern Medical Center at RedBird 3450 W. Camp Wisdom RoadDallas, Texas 75237 214-214-5810 Directions to Vascular Medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center at RedBird, Dallas Parking Info for Vascular Medicine
Vascular Medicine
at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Coppell 2999 Olympus Blvd., 3rd FloorCoppell, Texas 75019 469-647-4446 Directions to Vascular Medicine at UT Southwestern Medical Center at Coppell, Coppell Parking Info for Vascular Medicine