Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis
New Patient Appointment or 214-645-4673
Diagnosing pancreatic cancer can be difficult because of where the pancreas is located and because early symptoms can be unclear. However, finding it early is possible and can help with treatment.
It’s important to know that while some symptoms can be related to pancreatic cancer, they can also be caused by other, less serious issues. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Abdominal pain: A dull ache appears in the upper belly, especially after eating, and may spread to the back.
- Weight loss: People may lose weight without trying.
- Jaundice: Skin and the whites of the eyes may turn yellow, and urine may appear darker and stools lighter.
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting: Some people may feel sick to their stomach or throw up often.
- Fatigue: Patients may feel more tired than usual.
- Sudden-onset diabetes: A quick change in blood sugar levels could mean a problem with the pancreas.
Talk to our doctors if any of these signs get worse.
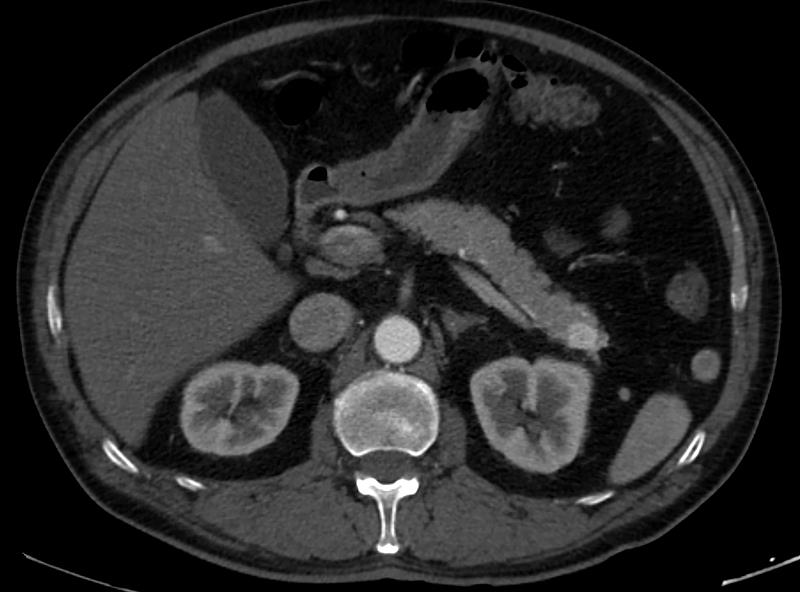
Diagnostic Tests for Pancreatic Cancer
In addition to a physical exam and health history, our doctors may use these tools and techniques to diagnose pancreatic cancer:
Blood tests: Blood tests can help check for liver function abnormalities, elevated pancreatic enzymes, and elevated tumor markers (CA 19-9), which can be signs of pancreatic cancer.
Imaging tests:
- CT scan: A computed tomography scan can create detailed images of the pancreas and surrounding organs.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging can provide more detailed images, especially if the tumor is small or difficult to detect with a CT scan.
Endoscopic ultrasound: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the esophagus and stomach to examine the pancreas.
Biopsy: If imaging tests suggest the presence of a tumor, a biopsy may be performed to collect a tissue sample for examination under a microscope. This is the only way to confirm a diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Genetic testing: Every patient with pancreatic cancer, regardless of personal or family history, will need genetic testing to determine whether the pancreatic cancer is hereditary. Some patients might need tumor testing to guide the conversations about treatment options.
Stages of Pancreatic Cancer
To plan treatment for pancreatic cancer, it is important to know the stage of the disease. Staging is a way of describing where the cancer is located, if or where it has spread, and whether it is affecting other parts of the body. Knowing the stage helps us decide what kind of treatment is best.
Pancreatic cancers are commonly staged into one of four categories, based on whether they are resectable (removable with surgery) and if or where they have spread.
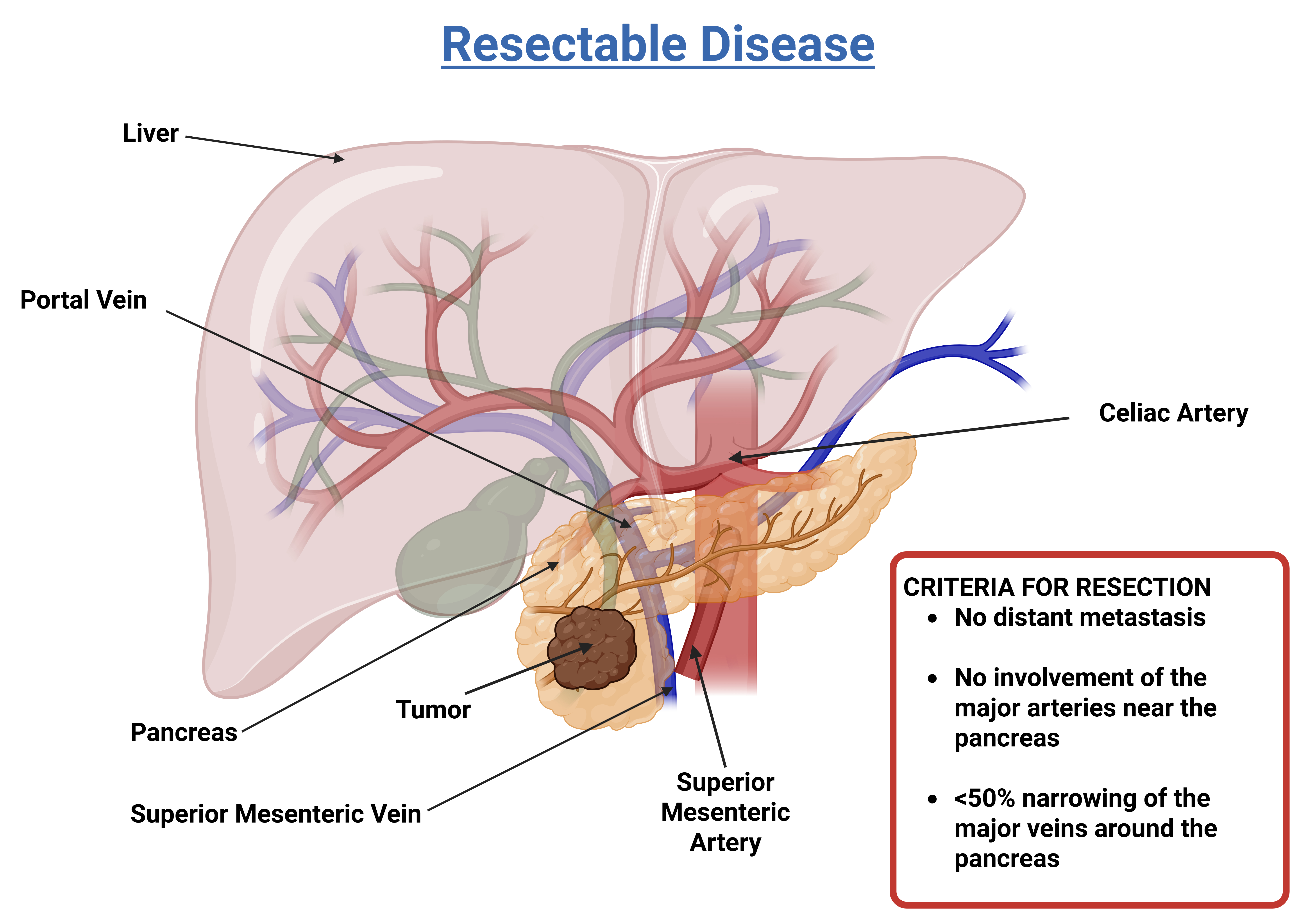
Resectable
This type of pancreatic cancer can be surgically removed (resected). The tumor might be located only in the pancreas or slightly beyond it, but it has not grown into important arteries or veins in the area or spread to other body systems or organs. Approximately 10 to 15 percent of patients are diagnosed with this stage.
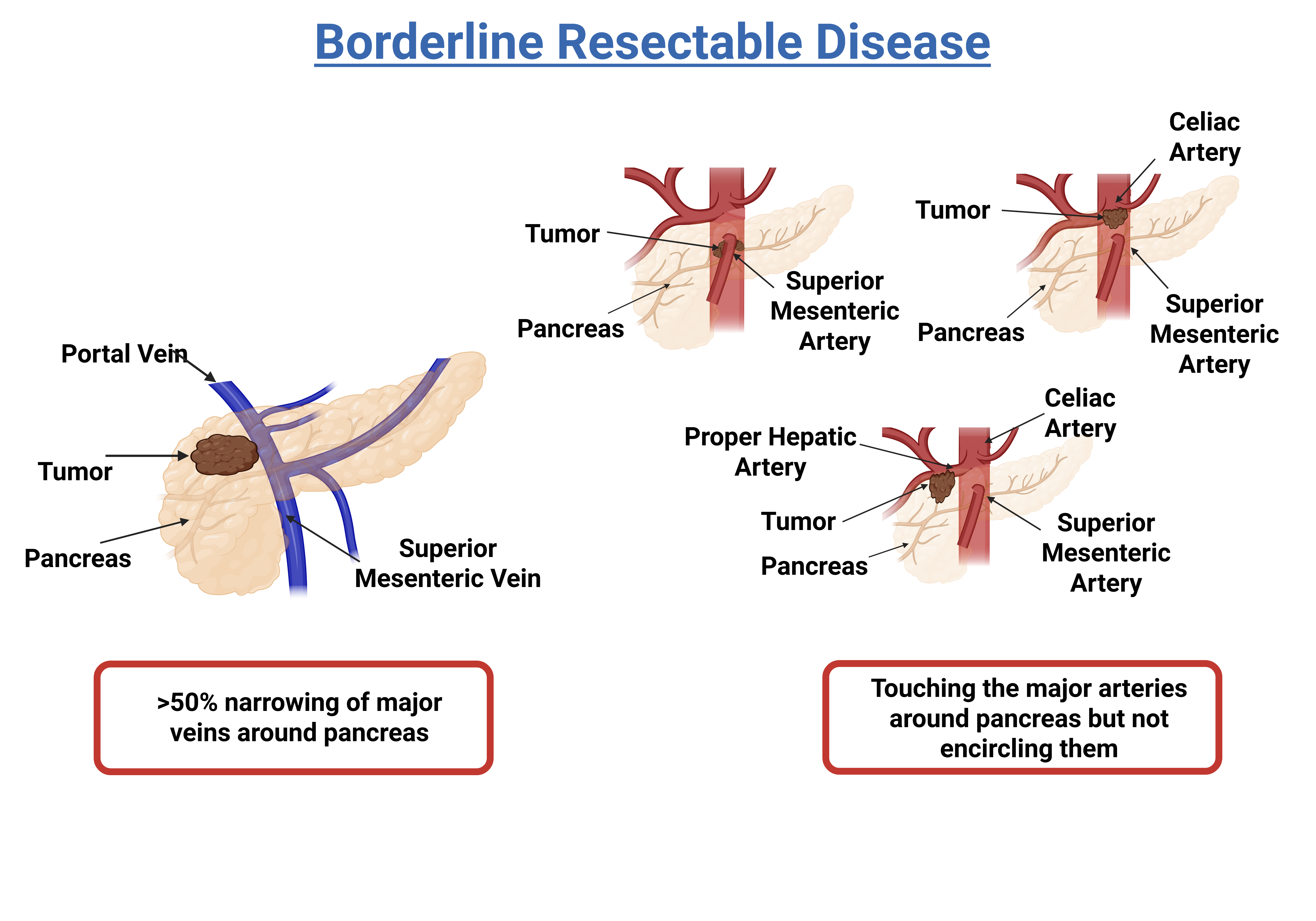
Borderline Resectable
This stage describes a tumor that can be difficult or impossible to resect when it is first diagnosed but might become resectable after being shrunk with chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Approximately 10 to 15 percent of patients are diagnosed at this stage.
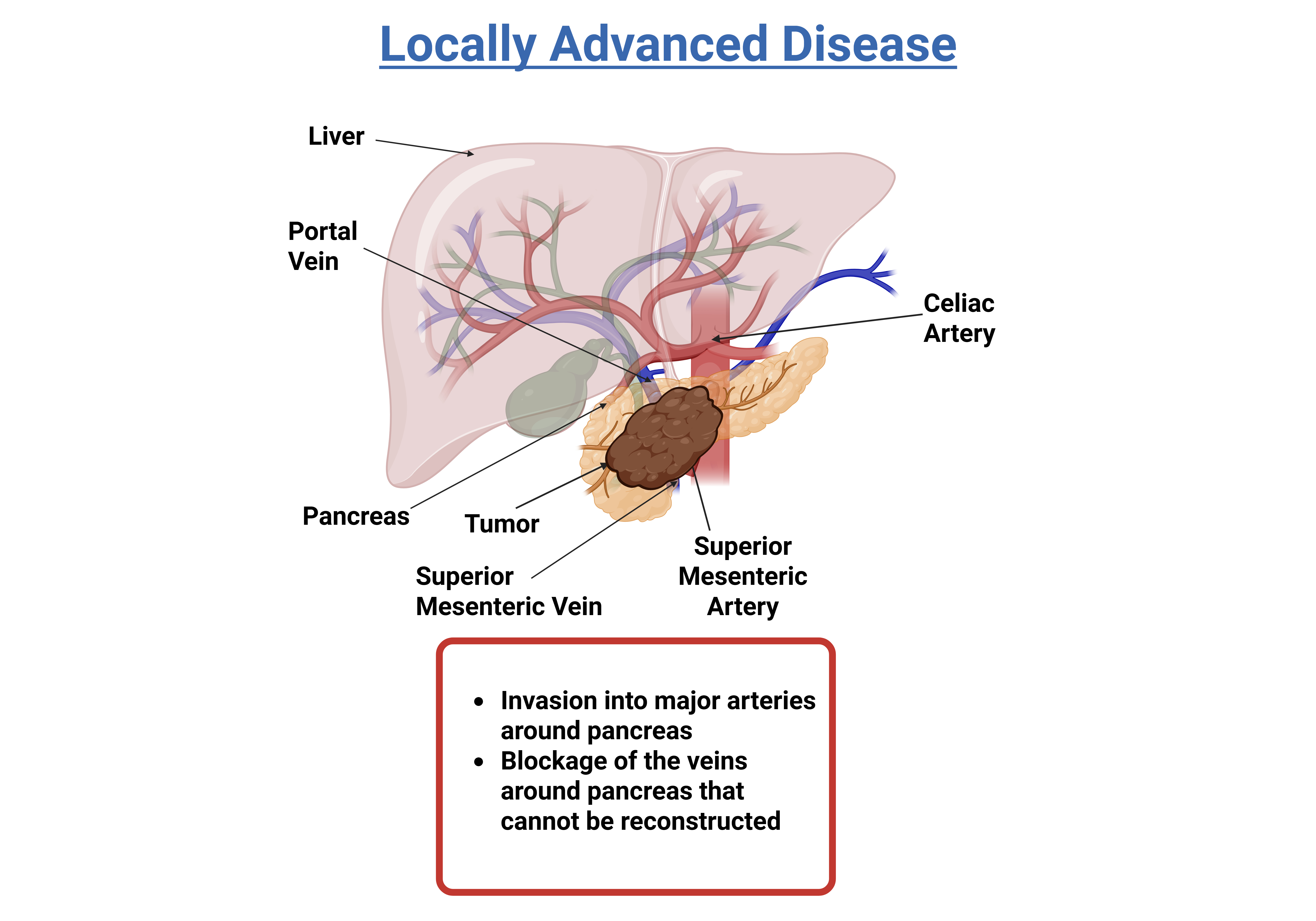
Locally advanced
The tumor is located only in the area around the pancreas, but it cannot be surgically removed because it has grown into nearby arteries, veins, or organs. However, it has not spread to any distant parts of the body. Approximately 10 to 15 percent of patients are diagnosed at this stage.
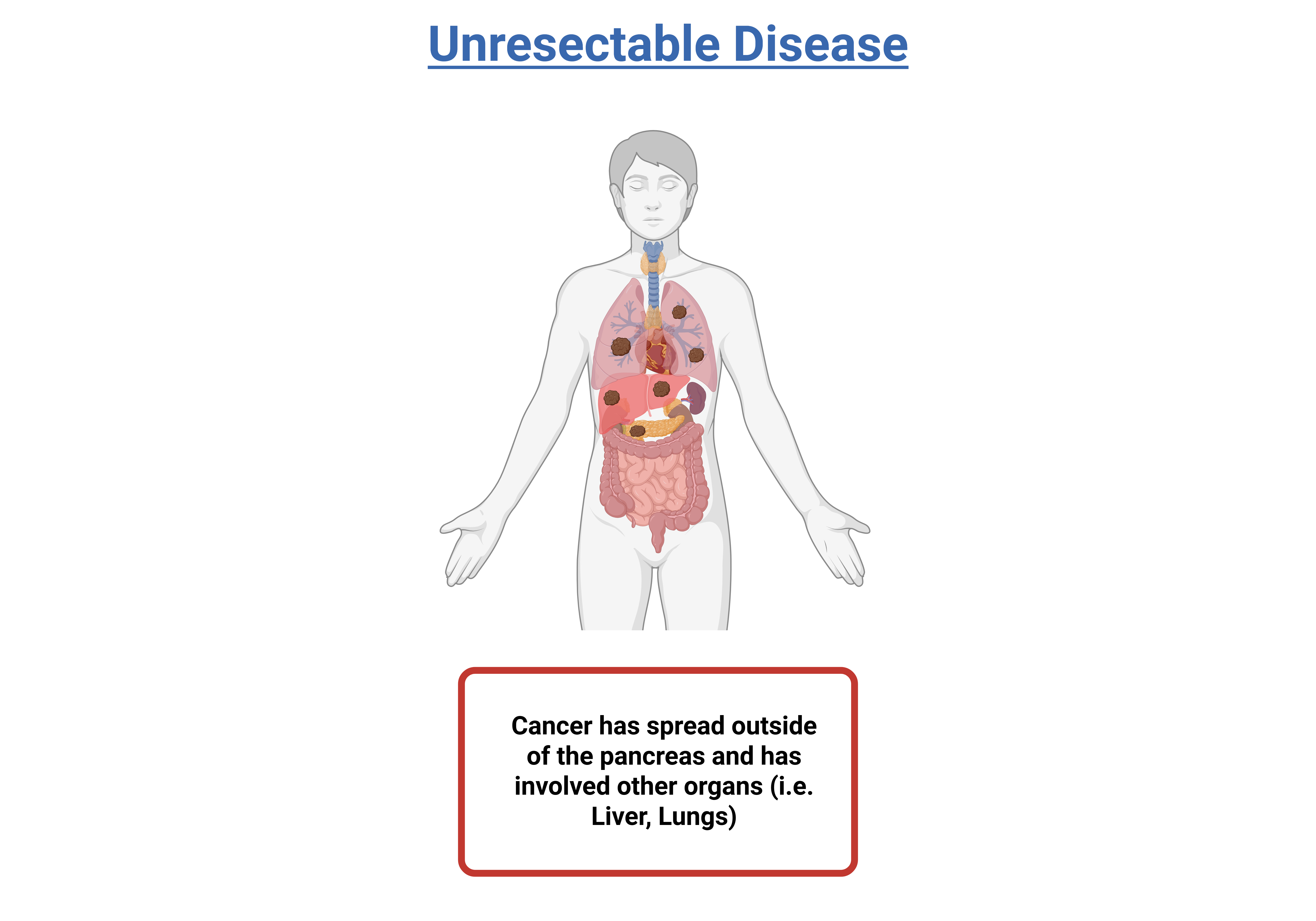
Metastatic
The tumor has spread beyond the area of the pancreas to other organs, such as the liver or distant areas of the abdomen. Approximately 60 to 70 percent of patients are diagnosed at this stage.

